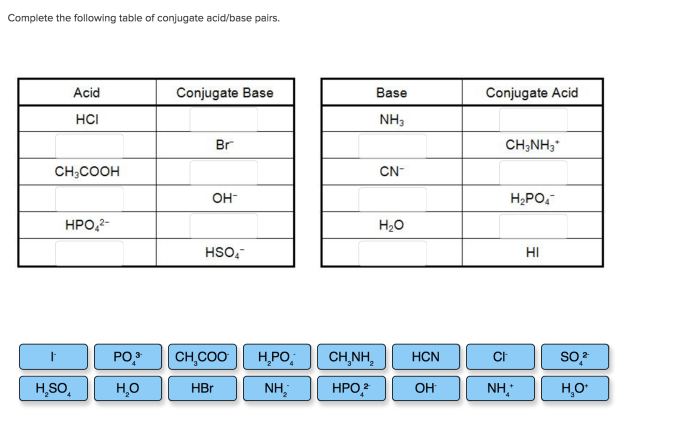
Complete the following table regarding acids and bases introduces a topic of paramount importance in the realm of chemistry. Acids and bases, ubiquitous in our world, play a pivotal role in shaping our understanding of chemical reactions and their applications.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of acids and bases, providing a thorough exploration of their properties, reactions, and significance.
Throughout this discourse, we will unravel the defining characteristics of acids and bases, examining their behavior in various contexts. We will investigate the pH scale, a crucial tool for measuring acidity and alkalinity. Furthermore, we will delve into acid-base reactions, exploring their mechanisms and the products they yield.
The process of acid-base titration will be meticulously explained, highlighting its applications in determining the concentration of unknown acids or bases.
1. Introduction
Acids and bases are two fundamental classes of chemical compounds that exhibit distinct properties and play crucial roles in various chemical reactions. An acid is a substance that donates a proton (H+) when dissolved in water, while a base is a substance that accepts a proton when dissolved in water.
Understanding the characteristics and reactions of acids and bases is essential for comprehending numerous chemical processes.
Acids and bases exhibit a range of properties. Acids typically taste sour, turn litmus paper red, and react with metals to produce hydrogen gas. Bases, on the other hand, taste bitter, turn litmus paper blue, and feel slippery to the touch.
The strength of an acid or base is measured on the pH scale, which ranges from 0 to 14. A pH of 7 is neutral, values below 7 indicate acidity, and values above 7 indicate basicity.
2. Acid-Base Reactions
Acid-base reactions are chemical reactions that involve the transfer of protons between acids and bases. These reactions are crucial in various chemical processes, such as neutralization, precipitation, and redox reactions.
- Neutralization reactions:These reactions occur when an acid and a base react in stoichiometric proportions to form a salt and water. The salt is a compound composed of the cation from the base and the anion from the acid. For example, when hydrochloric acid (HCl) reacts with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), it forms sodium chloride (NaCl) and water (H2O):
HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O
- Precipitation reactions:These reactions occur when two solutions containing ions of opposite charge are mixed, resulting in the formation of an insoluble solid precipitate. For example, when barium chloride (BaCl2) is mixed with sodium sulfate (Na2SO4), it forms barium sulfate (BaSO4) precipitate and sodium chloride (NaCl) remains in the solution:
BaCl2 + Na2SO4 → BaSO4 (s) + 2 NaCl
- Redox reactions:These reactions involve the transfer of electrons between reactants. Acids can act as oxidizing agents, accepting electrons and getting reduced, while bases can act as reducing agents, donating electrons and getting oxidized.
3. Acid-Base Titration

Acid-base titration is a laboratory technique used to determine the concentration of an unknown acid or base. The process involves gradually adding a known concentration of a base to a solution of the unknown acid until the reaction reaches the equivalence point, where the moles of acid and base are equal.
- Indicators:Indicators are substances that change color depending on the pH of the solution. They are used in acid-base titrations to signal the equivalence point. For example, phenolphthalein is a common indicator that turns pink at a pH of 8.3 or above.
- Calculation of concentration:The concentration of the unknown acid or base can be calculated using the formula:
C1V1 = C2V2
where C1 is the concentration of the known solution, V1 is the volume of the known solution added to reach the equivalence point, C2 is the concentration of the unknown solution, and V2 is the volume of the unknown solution.
4. Applications of Acids and Bases
Acids and bases have numerous applications in everyday life and industrial processes:
Acids
- Food and beverages:Acids, such as citric acid and acetic acid, are used as flavorings and preservatives in food and beverages.
- Batteries:Acids, such as sulfuric acid, are used as electrolytes in lead-acid batteries.
- Cleaning products:Acids, such as hydrochloric acid, are used in cleaning products to remove dirt and stains.
Bases, Complete the following table regarding acids and bases
- Soap and detergents:Bases, such as sodium hydroxide, are used in the production of soap and detergents.
- Paper production:Bases, such as calcium hydroxide, are used in the production of paper to neutralize acidic impurities.
- Construction:Bases, such as Portland cement, are used in construction as a binding agent.
Industrial applications
- Fertilizers:Acids, such as sulfuric acid, are used in the production of fertilizers.
- Pharmaceuticals:Acids and bases are used in the production of various pharmaceuticals.
- Petroleum refining:Acids and bases are used in petroleum refining processes to remove impurities and improve product quality.
5. Health and Safety Considerations: Complete The Following Table Regarding Acids And Bases

Acids and bases can be hazardous if not handled properly. It is important to take the following precautions when working with acids and bases:
- Wear protective gear:Always wear gloves, safety glasses, and a lab coat when handling acids and bases.
- Handle acids and bases in a well-ventilated area:Acids and bases can release harmful fumes, so it is important to work in a well-ventilated area.
- Never mix concentrated acids and bases:Mixing concentrated acids and bases can cause a violent reaction, resulting in splattering and burns.
- Dispose of acids and bases properly:Acids and bases should be disposed of according to local regulations. Never pour acids or bases down the drain.
Key Questions Answered
What is the pH scale?
The pH scale is a logarithmic scale used to measure the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. It ranges from 0 to 14, with 0 being the most acidic and 14 being the most alkaline (also known as basic).
What is the difference between an acid and a base?
Acids are substances that donate protons (H+ ions), while bases are substances that accept protons.
What is the purpose of acid-base titration?
Acid-base titration is a technique used to determine the concentration of an unknown acid or base. It involves adding a known amount of a base to an acid (or vice versa) until the reaction is complete, as indicated by a change in color of an indicator.