Embarking on the regulation of the lactase gene answer key, this discourse delves into the intricate mechanisms that govern lactase expression, shedding light on the genetic and environmental factors that shape this crucial digestive enzyme.
Lactase, the enzyme responsible for breaking down lactose, the sugar found in milk, is a subject of intense scientific inquiry due to its implications for lactose intolerance and its potential impact on human health.
Definition and Background
Gene regulation refers to the intricate mechanisms that control the expression of genes, determining when and to what extent specific genes are active within a cell. This process plays a crucial role in shaping cellular identity, function, and response to environmental cues.
The lactase gene, located on chromosome 2 in humans, encodes the enzyme lactase, which is responsible for breaking down the sugar lactose found in milk. Understanding the regulation of the lactase gene is essential for comprehending the genetic basis of lactose intolerance and its implications for human health.
Regulatory Mechanisms
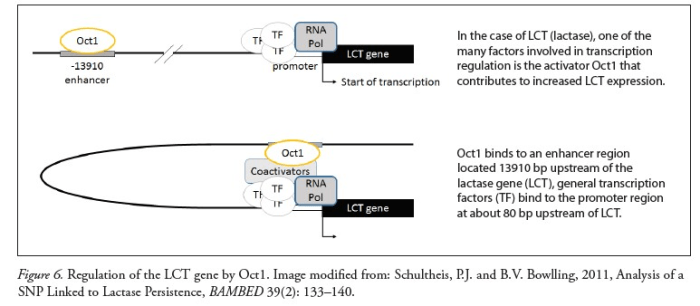
The regulation of the lactase gene involves multiple mechanisms that work in concert to fine-tune its expression.
Transcription Factors
Transcription factors are proteins that bind to specific DNA sequences, known as regulatory elements, and either promote or repress gene transcription. Several transcription factors, including GATA-6, HNF-1α, and Cdx2, have been identified as key regulators of lactase gene expression.
DNA Methylation
DNA methylation is a chemical modification of DNA that can influence gene expression. In the case of the lactase gene, DNA methylation of the promoter region has been associated with decreased gene activity, leading to reduced lactase production.
Histone Modifications
Histones are proteins that package DNA into chromatin, the structural material of chromosomes. Modifications to histones, such as acetylation and methylation, can alter chromatin structure and accessibility, thereby influencing gene expression. Histone modifications have been implicated in the regulation of lactase gene expression.
Environmental and Dietary Factors

Environmental and dietary factors can also influence lactase gene regulation.
Lactose Intake, Regulation of the lactase gene answer key
Lactose intake has a significant impact on lactase expression. Continuous exposure to lactose in the diet promotes lactase gene expression, while prolonged lactose deprivation can lead to a decline in lactase activity.
Gut Microbiota Composition
The composition of the gut microbiota, the trillions of bacteria that reside in the human digestive tract, has been linked to lactase gene regulation. Certain gut bacteria produce short-chain fatty acids, which have been shown to enhance lactase gene expression.
Genetic Variations and Polymorphisms: Regulation Of The Lactase Gene Answer Key
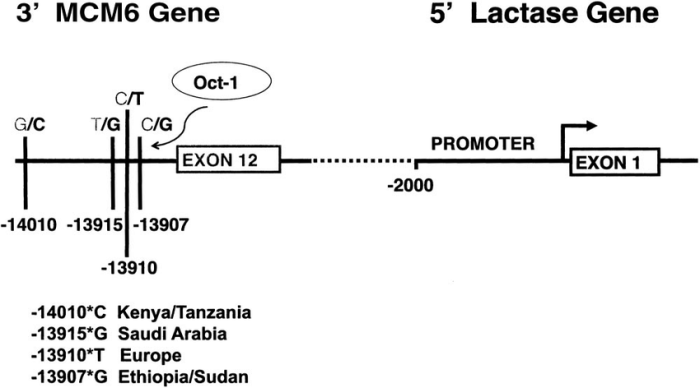
Genetic variations, particularly single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), can affect lactase gene regulation and contribute to lactose intolerance.
Lactase Persistence
Lactase persistence, the ability to digest lactose throughout life, is a genetic trait that is common in some populations. It is associated with a specific SNP in the lactase gene that results in the continued expression of lactase in adulthood.
Lactose Intolerance
Lactose intolerance, the inability to digest lactose, is caused by a decline in lactase activity. It is often associated with different SNPs in the lactase gene that lead to reduced or absent lactase production.
Clinical Implications
Understanding lactase gene regulation has important clinical implications.
Diagnosis of Lactose Intolerance
Genetic testing for lactase gene polymorphisms can aid in diagnosing lactose intolerance. Identifying individuals with specific genetic variants can help confirm the diagnosis and guide dietary recommendations.
Management of Lactose Intolerance
Understanding lactase gene regulation can inform the management of lactose intolerance. Individuals with certain genetic variants may benefit from dietary modifications, such as lactose-reduced or lactose-free products, to alleviate symptoms.
Future Research Directions
Research on lactase gene regulation continues to advance our understanding of lactose intolerance and its implications for human health.
Novel Regulatory Mechanisms
Ongoing studies aim to identify novel regulatory mechanisms that control lactase gene expression. Understanding these mechanisms could lead to new therapeutic approaches for lactose intolerance.
Personalized Nutrition
Future research may focus on developing personalized nutrition strategies based on individual genetic profiles. By understanding the genetic basis of lactase regulation, it may be possible to tailor dietary recommendations to meet the specific needs of individuals with lactose intolerance.
Helpful Answers
What is lactase persistence?
Lactase persistence refers to the continued expression of lactase enzyme activity into adulthood, allowing individuals to digest lactose without experiencing discomfort.
How is lactase gene regulation affected by diet?
Dietary lactose intake can influence lactase gene expression. Regular consumption of lactose-containing foods can stimulate lactase production, while prolonged lactose avoidance can lead to a decline in lactase activity.
What is the role of genetic variations in lactose intolerance?
Specific genetic variations, particularly in the LCT gene, have been associated with lactase persistence or lactose intolerance. These variations can impact the regulatory regions of the lactase gene, affecting its expression and activity.